Blockchain has catapulted from its origins as the foundation of Bitcoin to a groundbreaking technology with potential far beyond digital currencies. Decentralized ledger technology, as blockchain is formally known, offers unparalleled security, transparency, and efficiency, effectively rewriting the rules of data validation and sharing. This comprehensive guide demystifies blockchain for tech enthusiasts, investors, and business owners, paving the way for a deeper understanding of its mechanisms and vast capabilities.
Toc
Understanding Blockchain Technology
The Basics of Blockchain
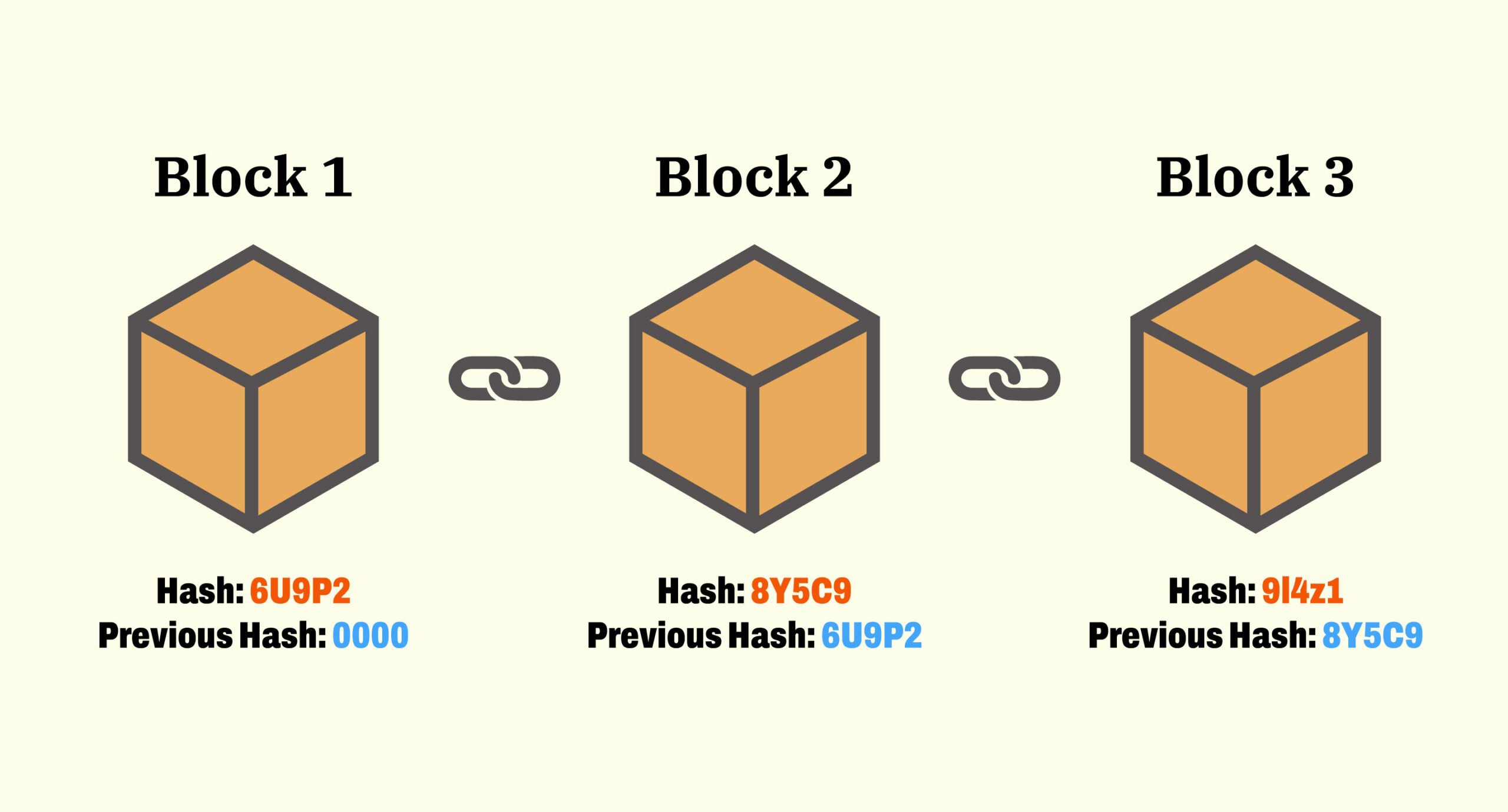
Blockchain is a complex yet robust system of recording information. It consists of blocks—units containing data, which, when verified by network participants known as nodes, are chained together using cryptographic principles. It’s a series of digital records that are tamper-resistant and immutable, all without the need for a central authority.
Decentralization and Its Importance
At blockchain’s core is decentralization, a stark contrast to the centralized systems employed by traditional banks and institutions. The distributed nature of the blockchain enhances resilience against attacks, improves security, and reduces dependency on any single entity, thus building a trustless environment.

Types of Blockchains
Different types of blockchains include public, private, and consortium blockchains, each serving diverse needs. Public blockchains are accessible to anyone, while private networks limit access to specific users. Consortium blockchains strike a balance, providing a more controlled environment with selected access. These different types of blockchains cater to a wide range of use cases, from storing and transferring value to tracking supply chains and managing digital identities.
The Rise of Cryptocurrencies
One of the most well-known applications built on blockchain technology is cryptocurrency. The first and most popular one is Bitcoin, which has gained significant traction in recent years. Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that operate independently of central authorities, providing greater control and ownership to users. With blockchain’s decentralized nature, cryptocurrencies offer a more secure and transparent way to transact, without the need for intermediaries.
Applications Beyond Finance
While cryptocurrencies have taken center stage, blockchain technology has given rise to numerous other applications beyond finance. Smart contracts, for example, allow for self-executing agreements between parties without the need for intermediaries. This has potential uses in areas such as supply chain management, real estate transactions, and intellectual property protection.
The use of blockchain technology also extends to voting systems, providing a more secure and transparent way to conduct elections. Additionally, it can be used in healthcare to securely store and share patient data, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Some companies are exploring the use of blockchain technology in digital identity verification. This would eliminate the need for multiple usernames and passwords across different platforms, making it easier for users to manage their online identities.

The Mechanisms Behind Blockchain
How Transactions Are Processed
Transactions within a blockchain utilize cryptographic techniques to maintain security. Consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake play crucial roles in validating transactions without a central authority, ensuring network integrity and trustworthiness.
When a new transaction is initiated, it is broadcasted to every node in the network. These nodes then compete to solve a complex mathematical problem, with the first one to find the solution being rewarded for their efforts.
Once the problem is solved, the verified transaction is added to a block along with other transactions. This block is then added to the chain of blocks, creating an immutable record of all past transactions.
As more blocks are added to the chain, it becomes increasingly difficult and resource-intensive to alter past transactions, making blockchain technology highly secure and tamper-proof.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
One of the main benefits of blockchain technology is its ability to create a decentralized system. This means that there is no single point of failure or control, making it less vulnerable to attacks and manipulation.
Additionally, the use of complex mathematical algorithms ensures that each transaction is secure and cannot be altered without being detected. This makes blockchain technology a highly trustworthy system for storing and transferring valuable information.
Another benefit is the transparency of blockchain transactions. As the ledger is publicly available, anyone can view the details of a transaction, creating a high level of accountability and reducing the risk of fraud or corruption.
In addition to its security features, blockchain technology also offers faster and more efficient transactions. With traditional methods, transactions may take days or even weeks to complete due to manual processes and third-party involvement. Blockchain technology eliminates these intermediaries, allowing for near-instant verification and transfer of assets.
Finally, blockchain technology has potential applications in various industries beyond finance. Its decentralized nature and ability to securely store and transfer data can be utilized in supply chain management, voting systems, digital identity verification, and more.

As the use of blockchain technology continues to grow and evolve, it has the potential to greatly impact the way we conduct transactions and share information. With its secure, transparent, fast, and versatile capabilities, blockchain is shaping up to be a game-changer in the world of technology. Organizations that embrace this innovative technology will have a competitive advantage in today’s ever-changing business landscape. So if you haven’t already, it’s time to start learning about blockchain and how it can benefit your organization or personal life.
Smart Contracts and DApps
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Decentralized Applications (DApps) use smart contracts to create a novel type of service or application that’s more resistant to censorship and downtime. By automating tasks and eliminating the need for intermediaries, blockchain-based smart contracts and DApps offer a cure to many of the issues plaguing traditional systems.
Transparency and Security
One of the key benefits of blockchain technology is its transparency. Transactions made on the blockchain are recorded on a distributed ledger, making them publicly available for anyone to verify. This level of transparency ensures that there is no room for fraud or manipulation, leading to increased trust in the system.
Additionally, blockchain technology offers unprecedented security. The decentralized nature of the network means that there is no central point of failure, making it nearly impossible for hackers to compromise the system. With sensitive data and information becoming increasingly vulnerable in today’s digital world, this level of security provided by blockchain technology is crucial.

In the world of cryptocurrency, security is of utmost importance. With large amounts of money being transferred and stored on the blockchain, it is essential to have a system that can withstand attacks from malicious actors. Blockchain technology employs advanced cryptographic techniques to ensure the safety and integrity of transactions.
Moreover, with traditional financial institutions being vulnerable to cyberattacks, many individuals and businesses are turning to cryptocurrencies as a more secure alternative. The immutable nature of blockchain technology means that once a transaction has been recorded on the ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted. This eliminates the risk of fraud or tampering, providing users with peace of mind when conducting transactions.
As cryptocurrencies continue to gain traction in mainstream society, the need for robust security measures becomes even more pressing. Thankfully, blockchain technology provides a solution with its decentralized and transparent structure. Instead of relying on a central authority to validate transactions, blockchain networks are maintained by a network of nodes, making it nearly impossible for cybercriminals to compromise the system.
Furthermore, the transparency of blockchain technology allows for greater trust between parties involved in a transaction. As all transactions are recorded on an open ledger and can be viewed by anyone, there is no room for hidden fees or deception. This level of transparency promotes accountability and fosters trust within the cryptocurrency community.
In addition to security and transparency, blockchain also offers speed and efficiency in conducting transactions. Traditional financial institutions often have lengthy processing times for international transactions, which can be costly and inconvenient. With cryptocurrencies utilizing blockchain technology, transactions can be completed in a matter of minutes, regardless of geographical location. This makes it an ideal solution for businesses and individuals who need to conduct fast and secure international transactions.

Another benefit of blockchain technology is its potential to revolutionize industries beyond finance. The decentralized nature of blockchain allows for the creation of decentralized applications (Dapps) that can disrupt various sectors such as healthcare, supply chain management, and even voting systems. These Dapps operate on a peer-to-peer network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs while increasing efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations
Blockchain technology is not without its limitations. Issues like scalability create bottlenecks in transaction processing, and the significant energy consumption of certain consensus models, especially Proof of Work, raise environmental concerns. Additionally, the lack of standardization and regulatory frameworks can hinder widespread adoption and disrupt the interoperability between different blockchain networks.
Security is another major concern in the world of blockchain. While the technology boasts strong encryption and immutability, it is still vulnerable to hacks and attacks. The decentralized nature also means that there is no central authority or governing body to regulate transactions, making it challenging to address issues like fraud or dispute resolution.
Future Outlook
Despite these challenges, the potential applications of blockchain continue to grow. As more industries recognize its benefits and work towards solutions for its limitations, we can expect to see widespread adoption of this revolutionary technology. Governments around the world are also exploring ways to integrate blockchain into their systems, leading to a more transparent and efficient administration. Additionally, the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) has opened up a whole new realm of possibilities for blockchain, allowing for innovative financial products and services to be created on a decentralized platform.

Some potential future applications of blockchain include supply chain management, voting systems, and identity verification. With its ability to securely store data in an immutable ledger, blockchain can help streamline processes and increase transparency in various industries. For example, in supply chain management, blockchain can track and verify the origin and authenticity of products, reducing the risk of counterfeit goods entering the market.
In terms of voting systems, blockchain can provide a secure and transparent way to record votes without the need for a central authority. This could potentially eliminate issues with voter fraud and increase trust in democratic processes
Blockchain Applications Beyond Cryptocurrencies

Financial Services
Blockchain is revolutionizing financial services with applications like cross-border payments, remittances, and the burgeoning field of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), all promising more inclusive financial systems. With blockchain, transactions can be conducted faster and at a lower cost than traditional methods, making it an attractive option for businesses and individuals alike.
Supply Chain Management
One of the most promising use cases for blockchain is in supply chain management. By using distributed ledger technology, companies can track and verify the origin and authenticity of products, reducing the risk of counterfeit goods entering the market. This not only protects consumers but also helps businesses maintain their reputation and brand integrity.
Voting Systems
Blockchain has shown potential in revolutionizing the voting process by providing a secure and transparent way to record votes without the need for a central authority. This could potentially eliminate issues with voter fraud and increase trust in democratic processes.

Healthcare
The healthcare industry is another area where blockchain is being explored for its potential uses. By securely storing and managing patient data on a distributed ledger, healthcare providers can improve efficiency and accuracy in medical record keeping. This can also lead to better coordination between different healthcare entities and ultimately improve patient care.
Real Estate
Real estate transactions are often complex and involve many intermediaries, which can result in delays and added costs. With blockchain technology, the entire process from buying to selling a property could be streamlined, making it more efficient and cost-effective. Additionally, property ownership records stored on the blockchain would be tamper-proof, reducing the risk of fraud.
Identity Management
Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize how we manage our digital identities. With traditional systems, personal information is vulnerable to hacking or misuse by centralized authorities. Using blockchain, individuals could have control over their own identity data and choose who has access to it. This would greatly increase security and privacy, while also simplifying the process of verifying identities for various transactions.

Supply Chain Management
The supply chain industry is notorious for its lack of transparency and accountability. Blockchain technology offers a solution by creating an immutable record of every step in the supply chain, from production to delivery. This allows for greater traceability and authenticity in goods, making it easier to identify and eliminate counterfeit products.
Medical Records
The healthcare industry is another area that can greatly benefit from blockchain technology. By storing medical records on a secure, decentralized network, patient data remains confidential and can be easily accessed by authorized parties. This eliminates the need for paper records and reduces the risk of errors or fraud.
Property Ownership
Blockchain has the potential to streamline the process of property ownership by creating a digital record of all transactions. This would eliminate the need for third-party intermediaries and reduce costs associated with buying and selling properties. Additionally, it would make it easier to verify ownership and prevent fraudulent activities like title fraud.
Other Emerging Applications
Blockchain’s potential stretches to healthcare for secure patient data management, real estate for streamlining transactions, and the art world through digitized collectibles or NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens). It also has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing a transparent and traceable ledger for tracking goods.

The Future of Blockchain Technology
Emerging Trends
Blockchain’s seamless integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) sets the stage for a highly interconnected future where data exchange and automation reach new heights. The rising popularity of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and the trend towards asset tokenization not only revolutionize digital ownership but also pave the way for innovative forms of creativity and investment opportunities in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain technology is continuously evolving as governments and regulatory bodies grapple with the complexities of this innovative space. These regulatory challenges play a pivotal role in shaping the adoption rates and level of innovation within the blockchain industry. It is crucial to establish balanced regulatory frameworks that not only encourage growth and development but also safeguard the interests of all stakeholders involved in the blockchain ecosystem. Such frameworks can provide the necessary stability and confidence for businesses and individuals to explore the full potential of blockchain technology.

Blockchain and Society
Potential societal impacts of blockchain technology are multifaceted and nuanced. Beyond its capacity to drive social change, it also holds promise in revolutionizing various sectors such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. However, as we navigate this digital landscape, it is crucial to carefully deliberate on the ethical implications that arise. Questions surrounding data privacy, security, and governance must be addressed to ensure that blockchain adoption is not just efficient but also equitable. Moreover, the potential risk of widening the digital divide must not be overlooked. Therefore, a holistic approach to blockchain adoption is imperative, one that is inclusive of diverse perspectives and considerate of the broader societal implications.
Real-World Applications
From revolutionizing supply chain management to enhancing the integrity of voting systems, blockchain technology has found applications across diverse industries. Its unparalleled potential for fostering transparency, streamlining operations, and bolstering security has garnered significant interest and investments from a wide spectrum of stakeholders, including businesses, governments, and technology enthusiasts alike. The decentralized nature of blockchain, coupled with its immutable ledger system, has the capacity to reshape traditional processes and pave the way for a more secure and efficient future in various sectors.
Preparing for a Blockchain-Driven World
To thrive in a future shaped by blockchain, acquiring relevant skills and knowledge is fundamental. Businesses and governments alike are recognizing the need to adapt to this emerging technology. The demand for blockchain professionals is expected to increase significantly in the coming years.

Education and Training Opportunities
As the demand for blockchain expertise rises, so do opportunities for education and training. Online courses, certifications, and workshops are becoming more prevalent, providing accessible ways to learn about blockchain technology and its applications.
Collaboration and Integration
The potential of blockchain can only be fully realized through collaboration between different industries and sectors. By integrating blockchain into existing systems, businesses can streamline processes and reduce costs while improving security and transparency.
Investing in Blockchain
With the growing adoption of blockchain technology across various industries, investing in this emerging market has become increasingly attractive. As with any investment opportunity, it is important to thoroughly research and understand the risks associated with cryptocurrency investments.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology harbors the power to fundamentally alter how we conduct transactions, govern data, and manage digital identity across multiple sectors. Its success hinges on continuous innovation, responsible regulation, and widespread education. By recognizing and cultivating the myriad benefits and applications of blockchain, society can unlock a future rich with untapped possibilities, ultimately signalling a new era in the digital realm










