The world of cryptocurrency is a continuously evolving financial frontier, with Bitcoin remaining the undisputed kingpin. It has become not just a digital currency but a symbol of the potential for technology to redefine our understanding of money. In this edition of ‘Bitcoin Price Prediction’, we gaze into the future landscape of Bitcoin’s valuation, probing the many layers that shape its market dynamics as we head into 2024 and beyond.
Toc

What is Bitcoin?
At its core, Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, founded by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. It operates on a peer-to-peer network, utilizing blockchain technology to maintain a secure and public ledger of transactions. It is void of any central authority, such as governments or banks, making it a purely market-driven commodity.
Analyzing Bitcoin Price Fluctuations
Bitcoin’s price, as of today, is [insert current price], seeing fluctuations that are a testament to the volatile yet fascinating world of cryptocurrencies. This price is a result of a myriad of factors, including market sentiment, investor behavior, regulatory news, technological advancements, and macroeconomic trends.
The Driving Forces Behind Bitcoin Prices
Several factors play pivotal roles in the market value of Bitcoin. These include:
- Supply and Demand Dynamics: With a capped supply of 21 million coins, Bitcoin portrays the classic economic scenario where limited supply meets growing demand.
- Market Sentiment: News developments, global events, and investor sentiment significantly impact Bitcoin’s price swings.
- Regulatory Changes: Government policies and regulations can either create an environment for growth or curb its expansion.
- Technological Innovations: Upgrades and forks in Bitcoin’s network influence confidence in the currency’s utility and security.
Historical Trajectory of Bitcoin Prices
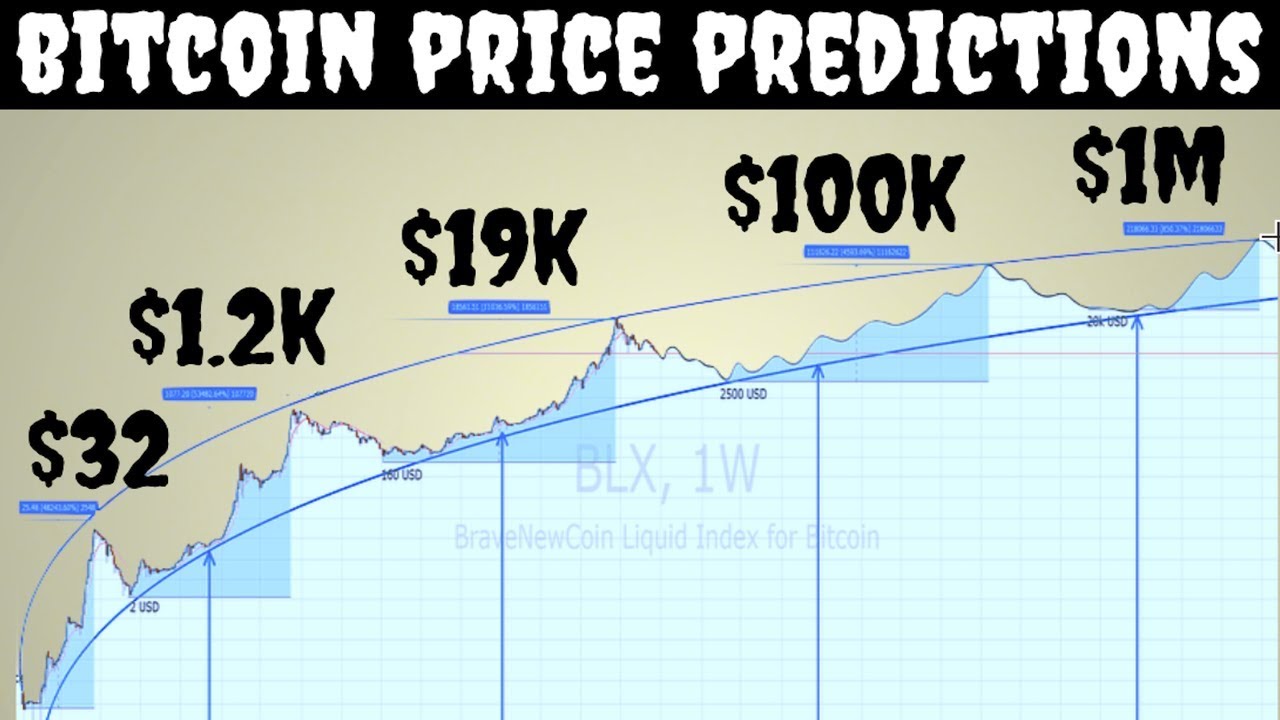
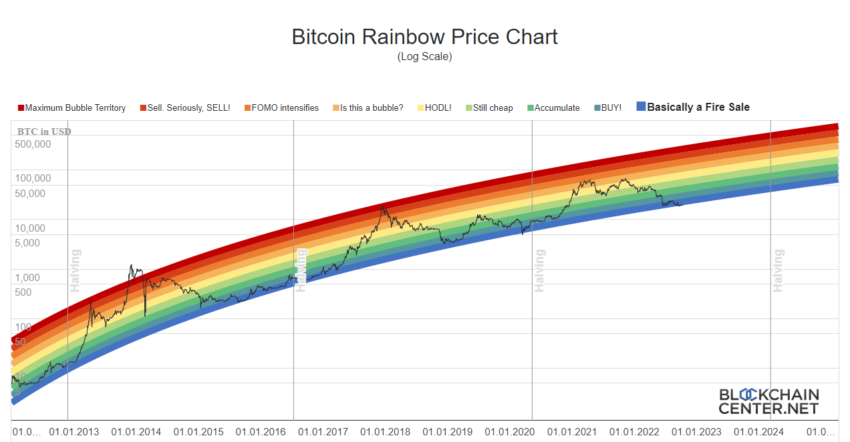
Looking at the history of Bitcoin prices, we see a pattern of exponential climbs followed by corrections. It has experienced several significant bull runs, notably in late 2017 and again in early 2021, each followed by steep retractions, demonstrating the volatile but generally upward trend over the long term.
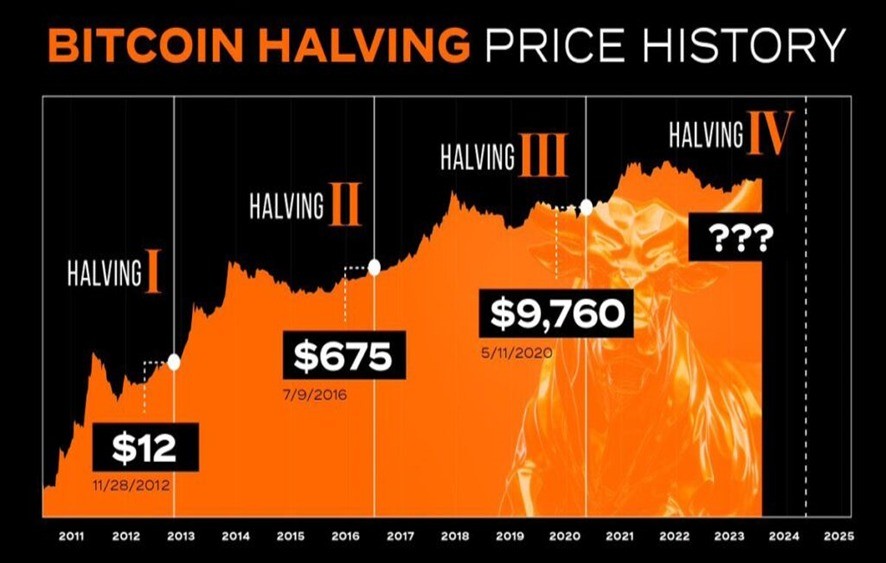
The Impact of Bitcoin Halving Events
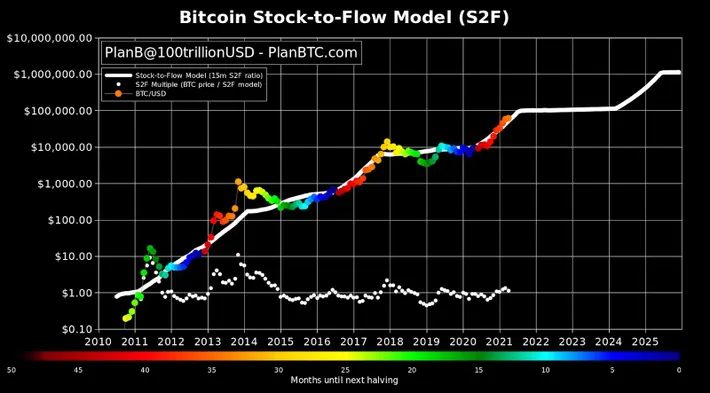
One unique aspect of Bitcoin is the halving event, which occurs approximately every four years, cutting the reward for mined blocks in half. Historically, these halving events have preceded substantial price increases, as they reduce the rate at which new bitcoins are released, underpinning a rise in value due to the scarcity effect.
What is bitcoin halving?
Bitcoin halving is a fundamental part of Bitcoin’s protocol that reduces the reward for mining new blocks by half, approximately every four years. This mechanism is built into the code of Bitcoin to control the supply of new bitcoins entering the market and to mimic the scarcity and deflationary aspects of precious metals like gold.
How It Works
When Bitcoin was first created, the reward for mining a block was 50 bitcoins. According to Bitcoin’s source code, this reward halves every 210,000 blocks mined, a process that takes roughly four years to complete. As of my last update in April 2023, there have been three halvings:
- First Halving (2012): The reward decreased from 50 to 25 bitcoins.
- Second Halving (2016): The reward dropped from 25 to 12.5 bitcoins.
- Third Halving (2020): The reward was further reduced from 12.5 to 6.25 bitcoins.
The next halving is anticipated to occur in 2024, where the reward will be halved to 3.125 bitcoins per block.
Implications of Bitcoin Halving
Supply and Demand: The halving is designed to create a scarcity of new bitcoins, which can affect the price. According to the principles of supply and demand, the decreased supply of new bitcoins might lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price, assuming demand remains constant or increases.
Mining Profitability: Halvings can impact the profitability of mining. As the reward for mining a block decreases, miners with higher operational costs may find it less profitable to mine Bitcoin. This could lead to a consolidation in the mining industry or a push towards more efficient mining technologies.
Inflation Rate: Bitcoin’s inflation rate decreases with each halving, as fewer new bitcoins are created. This is in stark contrast to fiat currencies, where central banks can print money at will, potentially leading to inflation.
The Future
Bitcoin’s halving events are significant milestones in the cryptocurrency’s timeline, attracting attention from investors, traders, and the media. While the long-term effects of halving on Bitcoin’s price are subject to speculation, these events underscore Bitcoin’s deflationary nature and its distinction from traditional fiat currencies. As we approach future halvings, the crypto community watches closely to see how these dynamics play out in the evolving landscape of digital finance.
Bitcoin halving and Bitcoin price
Bitcoin halving is a significant event that directly impacts the supply of new Bitcoins entering the market. Theoretically, by reducing the rate at which new coins are generated, a halving should increase scarcity and, under the assumption of steady or growing demand, potentially lead to an increase in Bitcoin’s price. The rationale behind this effect involves several economic principles and market dynamics:
Supply and Demand
The most straightforward explanation lies in the basic economic principle of supply and demand. If the supply of a commodity (in this case, new Bitcoins) decreases while demand remains constant or increases, the price of the commodity is likely to rise. Bitcoin halvings reduce the supply of new bitcoins awarded to miners, which, over time, could increase the price if demand for Bitcoin continues to grow.
Speculative Anticipation
Historically, the price of Bitcoin has often increased leading up to and following a halving event, though not immediately. Part of this increase can be attributed to speculative anticipation. As traders and investors are aware of the potential impact of reduced supply on prices, they may buy Bitcoin in anticipation of future price increases, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy that drives up the price before the halving.
Miner Economics
Halving affects the revenue of miners, who secure the Bitcoin network by validating transactions and creating new blocks. When the block reward halves, miners receive 50% less Bitcoin for their efforts, potentially affecting their profitability. If the price of Bitcoin does not increase sufficiently to offset the reduced block reward, less efficient miners may be forced out of the market, leading to a temporary decrease in the network’s hash rate. However, the remaining miners would have a larger share of the mining rewards, and the decreased competition could make mining more profitable for them. This dynamic can contribute to a decrease in selling pressure from miners needing to cover operational costs, possibly leading to a price increase.
Long-Term Impact
The long-term impact of halving on Bitcoin’s price also considers the capped supply of 21 million Bitcoins. As halvings progressively reduce the rate of new Bitcoin creation, the increasing scarcity can contribute to long-term price appreciation, assuming Bitcoin remains in demand as a store of value, medium of exchange, or both.
Psychological Factors
The halving events also play a psychological role, reinforcing the perception of Bitcoin as a scarce asset. This scarcity appeal can attract long-term investors looking to hold Bitcoin as a digital counterpart to gold, which is also valued for its scarcity and has been used as a store of value for centuries.
Conclusion
While the economic principles suggest that halvings should positively impact Bitcoin’s price by reducing supply, the actual outcome depends on a complex interplay of market dynamics, investor sentiment, and external economic factors. The historical pattern has shown a tendency for Bitcoin’s price to rise following a halving, but it’s important to note that past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results, and cryptocurrency markets are notoriously volatile and unpredictable.

Looking Ahead: Bitcoin Price Predictions 2024-2035
Looking into the proverbial crystal ball, we take an informed stab at Bitcoin’s price trajectory from 2024 to 2035. Experts analyze trends, market cycles, and technological advancements to structure these predictions, although the inherent uncertainty of financial markets means they come with a degree of speculation.
Despite market fluctuations, the principle of scarcity and historical precedents suggest bullish trends post-halving events. Coupled with increasing industrial and institutional investment, as well as growing public awareness and acceptance, Bitcoin prices could soar to new heights. Some expert predictions speculate figures reaching [insert expert prediction range], while more conservative estimates place potential growth at [insert conservative prediction range].
In sum, Bitcoin retains its allure as a cutting-edge financial asset, determined largely by market forces and the sentiment of investors. The predictions we offer are grounded in analysis and historical trends, yet only time will reveal the real course Bitcoin’s price will take.

Predicting the future of Bitcoin’s worth is akin to gazing into a crystal ball—there are patterns and signs, but no certainties. The only sure thing is that Bitcoin will continue to play a pivotal role in the financial markets and the ongoing dialogue about the nature and possibilities of digital currencies.
For the savvy investor or the curious bystander, keeping an eye on the factors influencing Bitcoin’s price, remaining vigilant about market changes, and staying informed through trusted sources are key to understanding this digital currency’s trajectory. Whether its price rockets to the moon or steadies itself for sustainable growth, Bitcoin remains a fascinating watch as we move forward.
Please note that the mentioned predictions, figures, current prices, and expert opinions would need to be researched and updated at the time of writing to reflect the most accurate and current information. This article is also for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice.











